Understanding the Importance of 2-HYDROXY-6-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIDINE in Organic Chemistry
- 14 Mar, 2023
- 4371 views
Organic chemistry is a vast field that deals with the study of organic compounds, their properties, and their reactions. It has applications in various fields, such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science. One such important compound is 2-HYDROXY-6-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIDINE, which has gained significant attention in recent years due to its various applications in organic chemistry.
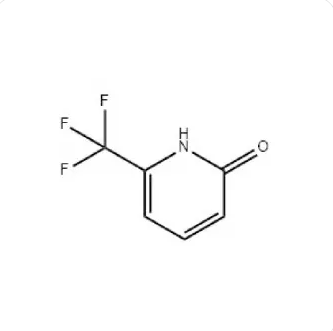
2-HYDROXY-6-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIDINE, commonly known as TFP, is a heterocyclic compound that contains a pyridine ring with a hydroxyl group at the 2-position and a trifluoromethyl group at the 6-position. TFP is a colorless liquid that has a melting point of -6°C and a boiling point of 96°C. TFP is a versatile compound that has a wide range of applications in organic chemistry.
One of the most significant applications of TFP is its use as a building block in the synthesis of various organic compounds. TFP can undergo various chemical reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic substitution, and addition reactions, which make it an ideal starting material for the synthesis of various organic compounds. TFP can be easily converted into a wide range of functional groups, such as esters, amides, and carboxylic acids, which are essential building blocks in organic chemistry.
TFP is also widely used as a catalyst in various organic reactions. It has been found that TFP can act as a Lewis acid catalyst in various reactions such as Friedel-Crafts acylation, aldol condensation, and Diels-Alder reactions. TFP has been shown to be an efficient and selective catalyst in many reactions, making it an ideal choice for use in organic synthesis.
Another important application of TFP is its use as a reagent in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. TFP has been found to be an important reagent in the synthesis of various drugs such as Aclidinium, a medication used for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and Siponimod, a medication used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. TFP has also been used in the synthesis of various insecticides and herbicides, which are essential in agriculture.
In addition to its various applications in organic chemistry, TFP has also gained attention for its unique properties. TFP has been found to exhibit antifungal and antibacterial properties, making it a potential candidate for the development of new antimicrobial agents. TFP has also been found to be an excellent ligand for various metal ions, which make it an ideal choice for the development of new catalysts for various organic reactions.
In conclusion, 2-HYDROXY-6-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PYRIDINE, commonly known as TFP, is a versatile compound that has a wide range of applications in organic chemistry. Its unique properties and reactivity make it an ideal starting material for the synthesis of various organic compounds, an efficient and selective catalyst for various organic reactions, and a potential candidate for the development of new antimicrobial agents and catalysts. TFP has gained significant attention in recent years due to its importance in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science, and it is expected to continue to be a valuable compound in the field of organic chemistry in the future.
- Category:
- Business
- No comments


